GASIFICATION MELTING SYSTEM
GTC GLOBAL is proposing the ultimate solution for medical and all other waste disposal problems. The Hydrolysis Gasification and Melting System (HHGMS) we offer is the most advanced and least polluting in the world. Emissions meet and exceed the limits for the State of California and permits were issued in the State of Louisiana to dispose of Normally Occurring Radioactive Materials (NORM). This technology generates its own fuel, a solution of Oxygen and Hydrogen in liquid water that is very safe, economical and burns at temperature that can exceed 3000® Celsius.
Our Hydrolysis technology is superior to the plasma technology in that it is less costly to procure and operate. It generates much less slag and ash. The produced slag is totally benign and can be added to the soil or construction materials. For larger plants, metal recovery units may be added to recover steel or any other metals.
HHGMS technology is ideal for cogeneration. The process heat generated may be recovered in a Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG) for generating high temperature steam for power generation, water desalinization or other processes. Applications for this technology are many. We are working with the owners of the patents to diversify the applications through the full spectrum, home heating to cement plants.
GTC GLOBAL (Environment)
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The system is used for all types of wastes: Municipal, Chemicals, Industrial, Toxic and other Hazardous, Medical, etc. This proposal was made to cover the medical waste only, however, the same is applicable on all other wastes.
The Hydrolysis Gasification Melting System (HHGMS) was invented to manage the radioactive wastes in US. There has been some units built for this matter, however, looking at the most sophisticated waste to deal with has made other wastes easy to manage through this system.
All types of wastes is used in the HGMS and electricity is generated.
Most wastes generated by hospitals and medical clinics are non-hazardous general wastes from hospital organization activities (i.e., including kitchen wastes, office materials, workshop residuals) and patient processing activities in wards which are not handling infectious diseases (i.e., first aid packaging, used but emptied disposable bed liners and diapers, disposable masks, pharmaceutical packaging, etc.). After source segregation of recyclables, disposal is typically by sanitary landfill.
Example:
MEDICAL WASTE TREATMENT
Potentially hazardous wastes from hospitals and clinics which have a pathogenic, chemical, explosive, or radioactive nature are called “medical wastes”. Medical wastes include the following:
- Pathological wastes (i.e., body parts, aborted fetus, tissue and body fluids from surgery; and dead infected laboratory animals);
- Infectious waste (i.e., surgical dressings and bandages, infected laboratory beddings, infectious cultures and stocks from laboratories, and all waste from patients in isolation wards handling infectious diseases);
- Sharps (i.e., needles, syringes, used instruments, broken glass);
- Pharmaceutical wastes (i.e., soiled or out-of-date pharmaceutical products);
- Chemical wastes (i.e., spent solvents, disinfectants, pesticides and diagnostic chemicals);
- Aerosols (i.e., aerosol containers or gas canisters which may explode if incinerated or punctured);
- Radioactive wastes (i.e., sealed sources in instruments, and open sources used in vitro diagnosis or nuclear medical therapy); and
- Sludge from any on-site wastewater treatment facilities may be potentially hazardous.
Pathological wastes should be destroyed by incineration under high heat (i.e., over 900o C with an afterburner temperature at over 800o C), although some countries require burial of human pathological wastes at official cemeteries for religious reasons. To reach these temperatures and have adequate afterburning and pollution control typically requires development of a regional medical waste facility. Smaller individual hospital or clinic incinerators may not be able to reach these temperatures and afterburning retention periods. Volatilized metals (such as arsenic, mercury, lead) and dioxins and furans could result from inadequate burning temperatures and retention periods.
It is very difficult for conventional incinerator to maintain 900o C. Even if it does, we would still end up with large mass that would have to be disposed of in a land fill. The same goes for sterilization steam. Even after treatment, it still needs the space in a land fill.
The most efficient, most direct and most feasible method to dispose of hazardous Medical waste is through the HGMS system we are offering. It is a one step solution that will eliminate the toxic legacy of waste, whether it is biological or radiological. GTC GLOBAL and its partners, in the USA, Japan and South Korea, possess the Engineering, Scientific and Management expertise to insure the success of this venture. We look forward apply this technology to other areas of Energy and environmental.
The HGMS furnace operates at a temperatures range between 1850®C to 3000®C to insure complete elimination of toxins in the emission regardless of the type waste feed. This is accomplished by continuously monitoring parameters, in the combustion chamber and the off-gas system, interlocked with automatic waste feed cutoff and the forced draft fans. The system is controlled by PLC and can operate practically unattended.
Our Understanding of the Situation:
Health authorities and environmental departments are working to reduce the amount of infectious waste around the world. Medical wastes in some circumstances are incinerated and Dioxins and Furans and other toxic gases air pollutants may be produced as emissions.
Exposure to Dioxins and Furans may lead to the impairment of the immune system, the impairment of the development of the nervous system, the endocrine system and the reproductive functions. The World Health Organization (WHO) has established a Provisional Tolerable Monthly Intake for Dioxins, Furans, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls. The unsafe disposal of medical waste poses public health risks. WHO estimated that in 2000, injections with contaminated syringes caused 21 million hepatitis B virus infections (which is about 32% of all new infections), which is a dangerous number.
Any unsafe disposal or incineration of the medical wastes causes health risk to the population, especially if it is incinerated under low temperature as most of the above toxic gases will be generated.
Objectives of the Project:
The objectives of the gasification and Melting (HGMS) project is the following:
- Safe handling of the medical waste.
- Gasification and Melting of the Medical Waste under high temperature (reaching 3000 C) without any emission of toxic gas. This includes the total elimination of all types of medical wastes, including the low radioactive materials, items that contain mercury and other toxic and hazardous materials.
- Daily testing of the byproduct material (residue) and make sure that it is toxic free.
- Use of the byproduct material as additive for cement strength.
- Possibility of generating electrical power from the HGMS upon request.
- Full compliance with HSE rules and regulations.
The management of health-care waste requires increased attention and diligence to avoid the substantial disease burden associated with poor practice, including exposure to infectious agents and toxic substances. HGMS provides an ultimate solution, which is safe and secure for the population.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
Technology Review
At the heart of this system, resides a patented technology known as the HS Technology (HST), the inventors managed to create a fuel from water. Unlike the conventional electrolysis of water to create pure O2 and H2, HST is a fuel, in solution with water, that is very safe and economical to produce, 2.4 Kwh electric energy are needed to produce one cubic meter of HST fuel. No special storage is required, the unit starts producing fuel the instant power is turned on.
Given the above, a cottage industry developed and started to coalesce around this fuel; Metal fabrication, Refractory, Burners, cutting tips, PLC and so on. More applications for the technology are surfacing:
- Waste to energy
- Medical Waste
- Intermediate and Low Level Radioactive Waste
- Gas & VOC Fume Waste
- Hazardous Waste
- Concentrated Liquid Waste
- MSW (Municipal Solid Waste)
- Facility Waste
- Sewage and Sludge
- Chemical and Industrial Wastes
Major Features
Aside from the unique fuel, many features distinguish this HST from any existing Hydrolysis Gasification Melting Technology (HGMS) or Incineration technology. To name a few;
Provide a clean economical solution to many hospitals and other clients, for disposal of dioxin types.
- Easy to control through automatic operation of series input and output of wastes.
- Efficient disposal of medical wastes in urban area with consistent results employing scientifically designed air pollution prevention devices.
- Excellent potential for heat recovery to generate clean energy.
- No auxiliary fuel is required. HST fuel provides the heat for gasification and production of synthetic gas then combustion of the produced gases provides the heat for melting. HST fuel remains ready on demand.
- Easy operation through automatic system from waste input to disposal completion.
Add on Features
A waste heat recovery steam generator and a condensing steam turbine may be added to the HGMS unit to generate electricity. A 10 ton per day unit can generate up to 2 Mega Watts (2000 Kilo Watt) of free electric power. On a larger system, low heat value waste such as Municipal Solid Waste, and NORM, may be combined with high heat value waste such as used tires to generate much more free energy that would be considered green because of the low or nearly no emissions.
Utilizing a high gradient metal separator, it is possible to recover useful metals such as iron, copper and Aluminum for recycling and reuse. All harmful heavy metals such as Pb, Cd, Cr6+, As, Se and Hg are well below 0.04% of the EPA soil environmental limit.
Physical Plant
For a 10 ton per day unit, 8000 SF metal building with 20’ will be required. The building will be engineered for sound and thermal insulation as well as ventilation. It shall have reinforced concrete foundation capable of handling the heaviest load to be expected plus the usual allowances for live and dead weight.
Facility will include operations offices, storage for spare parts and tools and showers for worker use, along with a test laboratory.
The plant shall include a storage facility of at least 3000 SF to store enough for a three day back log. Relative elevation of the two buildings will be such that it will gravity feed into the hopper of the unit.
Entire facility shall be security fenced and gated. Gate will be manned by security personnel around the clock.
Units GTC GOBAL Builds:
The following units GTC GLOBAL can build:
- 1 Ton Unit
- 5 Ton Unit
- 10 Ton Unit
- 20 Ton Unit
- 50 Ton Unit
- 100 Ton Unit
- 200 Ton Unit
OPERATION AND MANAGEMENT SECTION
Work Schedule
Ideally, the plant should operate 24 hours per day, 3 shifts with 8 hour each. The General Manager, Executive Assistant and accountant shall work 8 hours per day, 5 days per week. The Plant Superintendant, Lab Technician and Maintenance Forman shall work 8 hours per day, 6 days per week and be on call 24 hours per day, 7 days per week.
The Shift operator, Operator’s helper, Mechanic and Electrician shall work 8 hour shifts 5 days per week or 10 hour shift, 4 days per week or a combination of both. This will require having four or five crews for the entire operation. Maintenance Forman shall make the schedule and Plant Supervisor requires to approve it.
Organization Chart
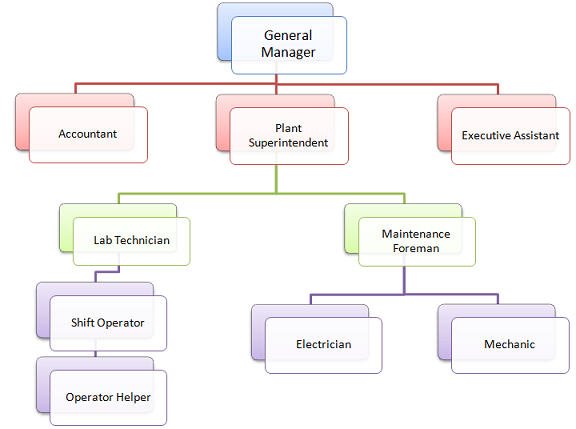
Management Structure
The Company by laws shall detail the management structure including number of board members, executive authority and distribution of profits.
OUR EXPERIENCE
Energy Recovery

The HGMS technology was primarily used for low level of radioactive wastes. Its main objective therefore typically was to eliminate the waste without the effort to use the excess of heat that can be used for power generation. However, some modification has been made since the building of the first HGMS unit in a way to economically generate electrical power, which is not wasted and is very practical to connect to the power generator network in any city.
Metals as well can be extracted and treated in order to reuse. It therefore, engineered the unit to utilize almost all byproducts, whether metals or the extra energy to use. Even the fly ash is inert and can be used to mix with soil or add to the cement to increase its compressive strength. The system is very flexible to use for all different types of waste, from municipals to radioactive. With the HGMS technology there is no need for landfill projects as the byproduct of the wastes are minimal. The unique type of product that HGMS technology market and sell is the renewable power. We believe the power generated from each unit built will qualify the can even replace lots of power generations around the world. A plant processing 100,000 tons of discarded material per year can generate between 20MW - 40MW, depending on material processed.
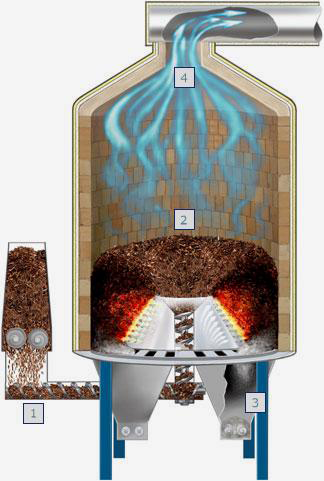
Environmental cleanup
The HGMS technology can totally replace the polluted lands or sites committed to landfill. The combination of hazardous and industrial wastes, organic polluted solid (oil spills and other petrochemicals), medical waste can be managed with the HGMS technology. The system will totally clean up the environment from the above wastes with all types of metals recovered and recycled. The system is self sterilizing, which yields zero gas and liquid and very low volume of solid byproduct. The HGMS technology requires minimum personnel to handle the waste as it feeds the system automatically. The system is the most restrict to the EPA rules and regulations in USA. The following materials are extracted from the HGMS unit:

All the organic materials are gasified and melted, while the inorganic materials will be collected and recycled. If heavily contaminated scrap metals that contain some organic materials is used, it will only gasify the organic part and melt the metal to reuse. This is not the case with incineration.
Stages for the Hydrolysis Gasification Plant:
- Assessment Stage: At this stage a full study is conducted with the collection of the infrastructure for the plant. This include the following:
- Total amount of wastes generated. The wastes include; hazardous, NORM, Medical, industrial toxic waste, and municipal.
- The procedure and process of currently handling the waste.
- Rules and regulations for the Emirate of Abu Dhabi and Federal Environmental law.
- The transportation law of the different waste types across different Emirates.
- Waste storage under current situation.
- Interview with the management who are handling and managing wastes under their supervisions.
- The emission of different toxic gases with the current incinerations used.
- Handling testing procedure to water and other samples in the laboratory.
- Type of the trucks used for transporting different wastes.
- Design Stage: At this stage a design of the plant will be made and presented to the authorities for their review and changes. This stage include the following:
- Size of the land required for the plant.
- Location of the plant and its distance from population.
- Capacity of the incinerator.
- Number of personnel required to run the plant.
- Daily maintenance for the plant.
- Size and type of the storage required for different waste type.
- The estimated costs for the plant of 10 and 20 tons capacities.
- Requirements for maintenance.
- Handling the waste transportation
- Use of the inert product after the incineration
- Transformation of the waste into fertilizers
- Design time: 35 – 40 working days.
- Implementation: At this stage the entire plant will be built based on the size and capacity required. The following are estimates of the land size and plant building for the 20 ton size incineration:
- Area required for building the plant: 12,000 square feet.
- Are required for storing the backlog for 3 days for the 20 ton plant: 3000 square feet.
- Personnel required to run the plant: Usually the plant is fully computerized and can be run by one engineer each shift of 12 hours. There is a requirement for 5 unskilled people to manage the site and store inside.
- Transportation: there will be two special trucks to carry the waste daily to the sight. Each truck requires a special trained driver along with two others who will handle the waste from the located place to the truck and to unload at the plant side. An extra truck is required as well for emergency which is smaller than the other two trucks.
- Estimated cost for the storage and plant building.
- Ventilation for the plant: there is special ventilation VOC that includes certain type of filtering system. The entire ventilation system comes with the plant.
- Personnel wares: We will provide all the personnel with special type of cloth to be fully protected according to OSHA regulations of USA.
- CFIL fiber filters are used to let the exhaust stay clean. The filters have 2 mg/m3 emissions with very stable long time operation. The filters are corrosion resistant, stands up to 900 degrees Celsius. Dust cake is built with time which is reversed via air blow.
- Cost for the entire project depends on the type of the wastes that are incinerated, whether it is Medical, Hazardous, Chemical, Industrial and/or municipal wastes. Usually, if more than one type of waste are to deal with, then storage should be built for each type of the waste. By building more than one storage different wastes can be treated based on the feeding and availability of the waste daily.
- Manufacturing time: 4 – 5 months.
- Pure water supply: 10 M3/hour X 30 Kg/Cm2, hour with two units.
- With Air vent pump: 10 M3 /hour X 6.7 Kg / Cm2.
- Operation Test: One month.
- Local Erection: One month.
TIME/COST SECTION
Project Schedule
Phase I: Delivery and Installation
The 10 ton per day unit will be delivered and ready to install in 3.5 - 5 months. The Engineering Procurement and Construction of the facility, including office space and storage, will take longer than 5 months. It is realistic to project 9 months for installation of the first 10 ton per day unit in order to be ready for commissioning.
Phase 2: Procurement
The procurement of larger unit, 20 tons per day or larger, needs to be installed to treat mixed waste. Municipal Solid Waste, Used Tires, NORM and Medical Waste. Along with HGMS, a Waste Heat Recovery Steam Generator and Steam Turbine/generator for a total capacity of 5MW of power should be procured. Engineering for the expansion facility and balance of plant should also be procured. Time requirement for this second should not exceed 9 months.
Estimated Cost
To have an estimate on each unit and recommended unit for your wastes type and amount please contact GTC GLOBAL main
offices in USA and Canada
Cell: +1 403 800 7265
|